

Right-click the Group Policy Object you want to configure, and then select Edit. On your Group Policy management computer, open the Group Policy Management Console. Use Group Policy to protect additional folders Select Add a protected folder and follow the prompts to add folders. Under the Controlled folder access section, select Protected folders.Ĭhoose Yes on the User Access Control prompt. Select Manage ransomware protection to open the Ransomware protection pane. Select Virus & threat protection, and then scroll down to the Ransomware protection section. Open the Windows Security app by selecting the shield icon in the task bar, or by searching for security in the Start menu. Use the Windows Security app to protect additional folders You can use the Windows Security app, Group Policy, PowerShell cmdlets, or mobile device management configuration service providers to add and remove protected folders.
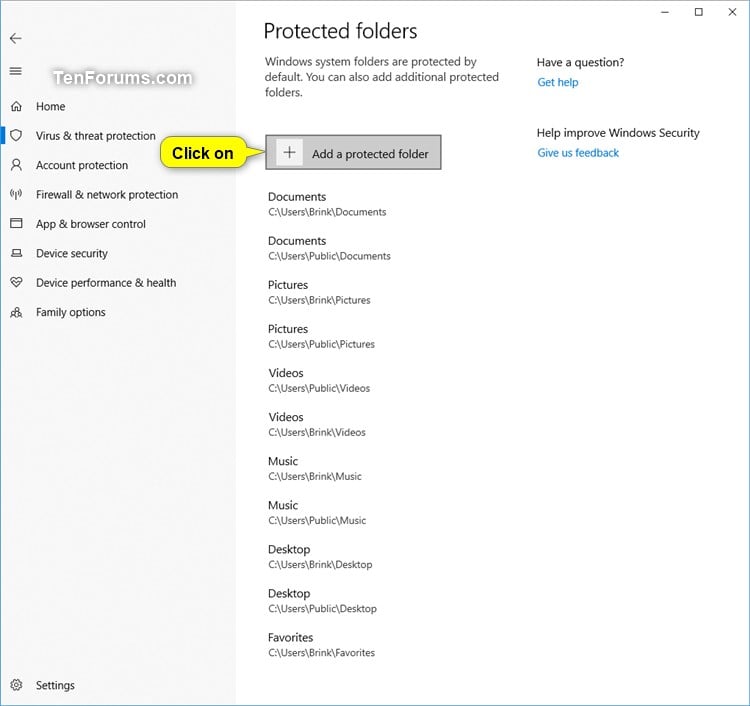
For information about using wildcards, see Use wildcards in the file name and folder path or extension exclusion lists. Environment variables and wildcards are supported. You can also specify network shares and mapped drives. You can add other folders to be protected, but you cannot remove the default folders in the default list.Īdding other folders to controlled folder access can be helpful for cases when you don't store files in the default Windows libraries, or you've changed the default location of your libraries.
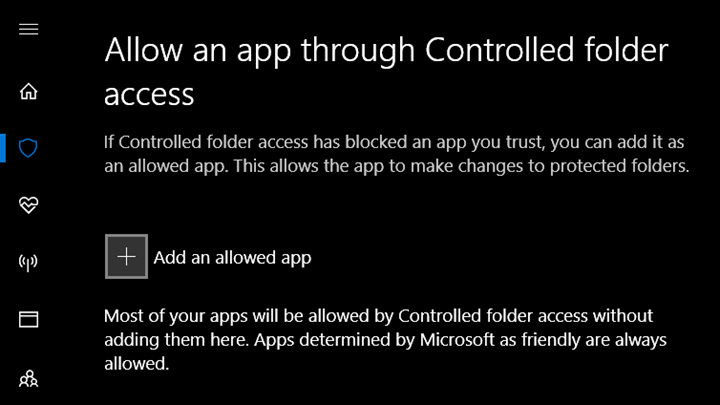
Protect additional foldersĬontrolled folder access applies to many system folders and default locations, including folders such as Documents, Pictures, and Movies. If controlled folder access impacts your organization's productivity, you might consider running this feature in audit mode to fully assess the impact. Sometimes, legitimate apps are blocked from making changes to your files. Controlled folder access monitors apps for activities that are detected as malicious.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
